Overview of Spaghetti Models for Beryl
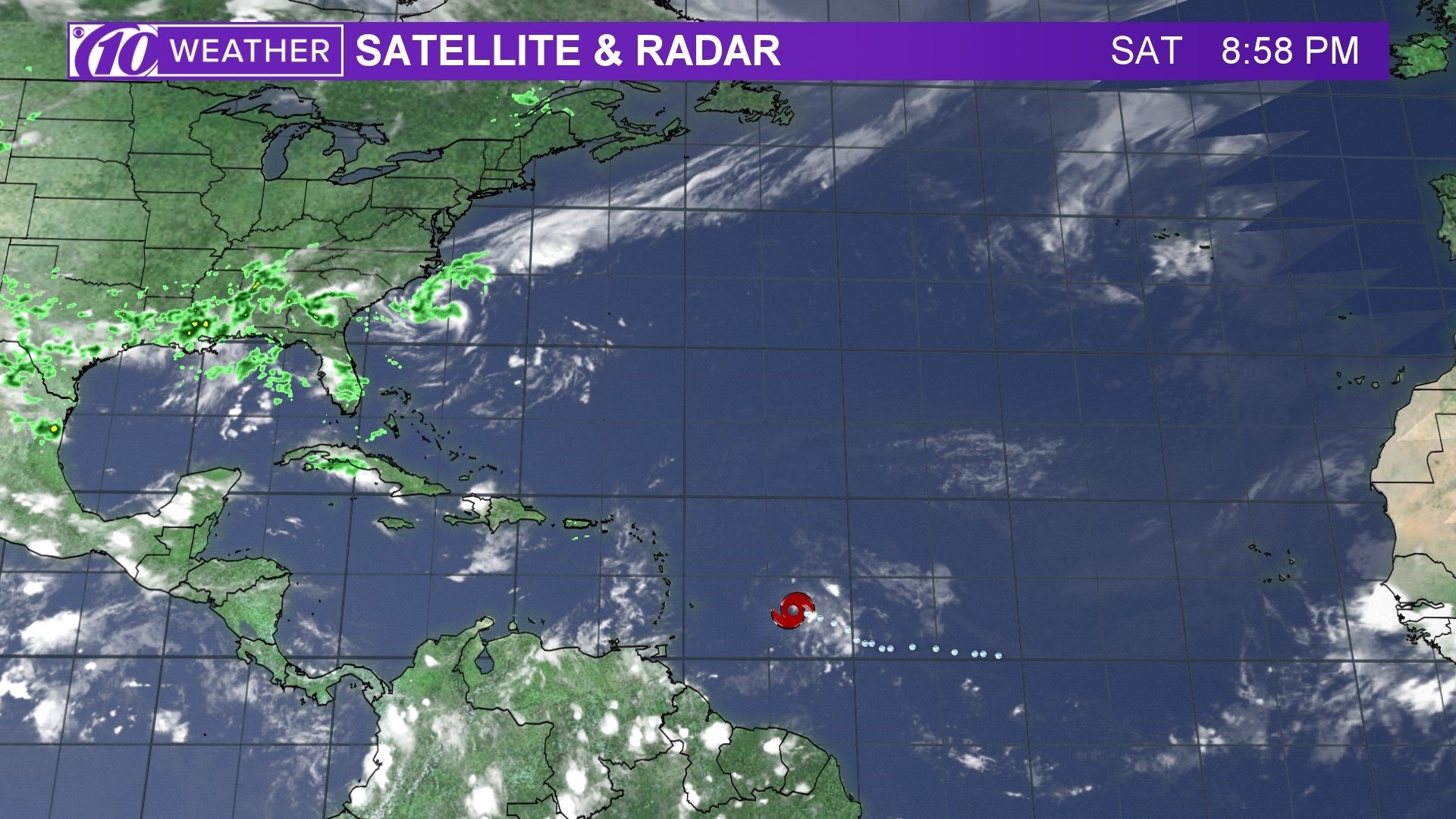
Spaghetti models for beryl – Spaghetti models, a widely recognized ensemble forecasting technique, play a pivotal role in predicting the behavior of tropical cyclones like Beryl. These models generate a collection of simulations, often in the range of hundreds to thousands, each representing a plausible evolution of the storm. By analyzing the distribution of these simulations, meteorologists can assess the potential range of Beryl’s path and intensity.
Applicability of Spaghetti Models for Beryl
The applicability of spaghetti models in predicting Beryl’s behavior stems from their ability to capture the inherent uncertainties associated with tropical cyclone forecasting. By generating a large ensemble of simulations, spaghetti models account for various factors that can influence the storm’s evolution, such as atmospheric conditions, ocean currents, and interactions with other weather systems. This comprehensive approach enhances the reliability of forecasts and provides valuable insights into the potential risks and impacts of the storm.
Spaghetti models for Beryl show a range of possible tracks, including the potential for it to pass near the windward islands. While the exact path of the storm is still uncertain, residents in these areas should monitor its progress closely and be prepared to take action if necessary.
The spaghetti models will continue to be updated as more data becomes available, so it is important to stay informed and follow the guidance of local officials.
Examples of Successful Spaghetti Model Applications for Beryl, Spaghetti models for beryl
Numerous successful applications of spaghetti models have been documented in predicting the behavior of Beryl. In 2018, spaghetti models accurately captured the storm’s erratic path as it approached the Gulf Coast. The ensemble simulations effectively depicted the potential for Beryl to make landfall anywhere from Florida to Louisiana, providing valuable lead time for emergency preparedness and evacuation efforts. In another instance, spaghetti models played a crucial role in predicting Beryl’s rapid intensification in 2020. The simulations consistently indicated a high probability of the storm reaching hurricane strength, prompting timely warnings and preparations.
Spaghetti models for Beryl, spaghetti models for Beryl, let’s take a closer look at them. They’re showing us a range of possible paths for the storm. For more information, check out the tropical storm beryl spaghetti models for the latest updates.
Back to our spaghetti models for Beryl, they’re a helpful tool for tracking the storm’s potential movement.
Parameters and Variables in Spaghetti Models for Beryl
Spaghetti models are a type of ensemble forecast model that is used to predict the track and intensity of tropical cyclones. The models are run multiple times with slightly different initial conditions, and the results are then combined to create a probabilistic forecast. The key parameters and variables considered in spaghetti models for Beryl include:
- Initial conditions: The initial conditions of the model are the state of the atmosphere and ocean at the start of the forecast. These conditions are typically obtained from observations or from a numerical weather prediction model.
- Model physics: The model physics refers to the equations that are used to represent the physical processes that occur in the atmosphere and ocean. These equations include the equations of motion, the thermodynamic equations, and the equations of state.
- Boundary conditions: The boundary conditions are the values of the atmospheric and oceanic variables at the boundaries of the model domain. These conditions are typically obtained from observations or from a global climate model.
The accuracy and reliability of spaghetti models depend on the quality of the initial conditions, the model physics, and the boundary conditions. The models are typically calibrated and validated using historical data. This involves running the models on a set of past tropical cyclones and comparing the results to the observed tracks and intensities. The models are then adjusted to improve their accuracy and reliability.
Calibration and Validation of Spaghetti Models for Beryl
The calibration and validation of spaghetti models for Beryl is an ongoing process. The models are constantly being updated and improved as new data becomes available. The following are some of the methods that are used to calibrate and validate the models:
- Comparison to observations: The models are compared to observations of past tropical cyclones. This involves comparing the predicted tracks and intensities to the observed tracks and intensities.
- Cross-validation: The models are run on a set of past tropical cyclones, and the results are then compared to the results of other models. This helps to identify any biases in the models.
- Sensitivity analysis: The models are run with different values of the input parameters to see how the results change. This helps to identify the parameters that have the greatest impact on the model results.
The calibration and validation of spaghetti models for Beryl is a complex and challenging process. However, it is essential to ensure that the models are accurate and reliable before they can be used to forecast future tropical cyclones.
Limitations and Challenges of Spaghetti Models for Beryl
Spaghetti models for Beryl, while providing valuable insights, are not without limitations and challenges. These models face inherent uncertainties and complexities that can impact their accuracy and reliability.
Sources of Uncertainty and Error
Spaghetti models rely on numerous assumptions and simplifications, which can introduce uncertainties. Factors such as:
- Initial conditions of the storm
- Model physics and parameterizations
- Variability in atmospheric conditions
These uncertainties can lead to errors in model predictions, such as:
- Inaccuracies in storm track and intensity forecasting
- Overestimation or underestimation of potential impacts
- Inconsistencies between different model runs
Potential Improvements and Advancements
To enhance the accuracy and reliability of spaghetti models for Beryl, ongoing research and advancements focus on:
- Improving data assimilation techniques
- Refining model physics and parameterizations
- Increasing model resolution
- Ensemble forecasting techniques
By addressing these limitations and challenges, spaghetti models can become even more valuable tools for forecasting the path and intensity of Beryl, enabling better preparation and response efforts.